簡単に機械学習を実装できるMediaPipeをgoogleが公開しています。
機械学習のライブラリは年々増えてきて、何を使うか悩んでしまいますね。実装の手軽さという点で優れているのが、googleのMediaPipeです。
手軽に、スマホやPCのカメラと連携して「画像認識」「物体検知」「セグメンテーション」ができてしまいます。今回は、MediaPipeの中で、「物体検知」のサンプルコードに解説を加えます。初心者向けになります。
MediaPipe Solutions guide | Google AI Edge | Google AI for Developers
はじめに
今回紹介するのは、こちらのコードです。Pythonのcocde exampleをクリックしてください。
colab上で動作するので便利です。

Object detection task guide | Google AI Edge | Google AI for Developers
このサンプルコードは、手持ちの画像データに、学習済みモデルを使って物体検知を行うコードです。
コード解説
準備
!pip install -q mediapipe==0.10.0mediapipeをインストールします
!wget -q -O efficientdet.tflite -q https://storage.googleapis.com/mediapipe-models/object_detector/efficientdet_lite0/int8/1/efficientdet_lite0.tflite物体検知の公開されている学習済みモデルをダウンロードします。Efficient det Liteです。
colabではなく、ローカルPCで実行する場合は、コマンドラインで先頭の”!”を外して実行しましょう。
物体検知の結果を可視化するための関数
#@markdown We implemented some functions to visualize the object detection results. <br/> Run the following cell to activate the functions.
import cv2
import numpy as np
MARGIN = 10 # pixels
ROW_SIZE = 10 # pixels
FONT_SIZE = 1
FONT_THICKNESS = 1
TEXT_COLOR = (255, 0, 0) # red
def visualize(
image,
detection_result
) -> np.ndarray:
"""Draws bounding boxes on the input image and return it.
Args:
image: The input RGB image.
detection_result: The list of all "Detection" entities to be visualize.
Returns:
Image with bounding boxes.
"""
for detection in detection_result.detections:
# Draw bounding_box
bbox = detection.bounding_box
start_point = bbox.origin_x, bbox.origin_y
end_point = bbox.origin_x + bbox.width, bbox.origin_y + bbox.height
cv2.rectangle(image, start_point, end_point, TEXT_COLOR, 3)
# Draw label and score
category = detection.categories[0]
category_name = category.category_name
probability = round(category.score, 2)
result_text = category_name + ' (' + str(probability) + ')'
text_location = (MARGIN + bbox.origin_x,
MARGIN + ROW_SIZE + bbox.origin_y)
cv2.putText(image, result_text, text_location, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_PLAIN,
FONT_SIZE, TEXT_COLOR, FONT_THICKNESS)
return imageここは、結果を可視化する関数です。opencvで画像に枠とテキストを書きます。
- 2~3行目:opencvとnumpyをインポート
- 5~9行目:設定値を変数でもっておきます
MARGIN:テキストを書く位置調整につかいます。バウンディングボックスから離す距離です
ROWSIZE:テキストを書く領域の高さです
FONTSIZE:テキストのサイズです
FONTTHICKNESS:テキストの太さです
TEXTCOLOR:テキストの色です。(255,0,0)は赤ですね。 - 12~14関数定義です。引数は
image 画像データ
detection_result 物体検知の結果 - 23行目:物体検知の結果分(検知した数分)繰り返します
- 25~28行目:bounding boxを書くところです。
- 25行目:boundingboxの情報を変数に保存。detection.bounding_boxと何回も書くのは面倒だからかな。。。
- 26行目:bounding boxの左上座標の取得xとy両方です
- 27行目:bounding boxの右下座標の取得。
x座標は、右上x+幅
y座標は、右上y+高さ です。 - 26と27行目は、opencvと、Efficient det Liteでboundingboxの表現方法が異なるため変換しています。opencvは左上と右下座標で表現で、Efficient det Liteは左上座標と幅・高さ。いつか画像処理業界で統一されないかと思っております。。。
- 28行目:opencvで画像に四角の枠を書きます
- 31~38行目:検知したラベルと、スコアをテキストで書くところです
- 31行目:検知結果を変数にいれておいて
- 32行目:検知した名前も変数にいれておきます
- 33行目:スコア(信頼度)を変数にいれておいて。
- 34行目:表示するテキストを作成しておきます
- 35行目:テキストを表示する場所を設定しておきます。(左上座標です)
- 37~38行目:テキストを表示します。引数は、対象画像、文字、位置、フォントの種類、フォントのサイズ、フォントの太さ です。
- 40行目:バウンディングボックスと、ラベル、スコアを書いた画像を返します。
テスト用の画像を準備
!wget -q -O image.jpg https://storage.googleapis.com/mediapipe-tasks/object_detector/cat_and_dog.jpg
IMAGE_FILE = 'image.jpg'
import cv2
from google.colab.patches import cv2_imshow
img = cv2.imread(IMAGE_FILE)
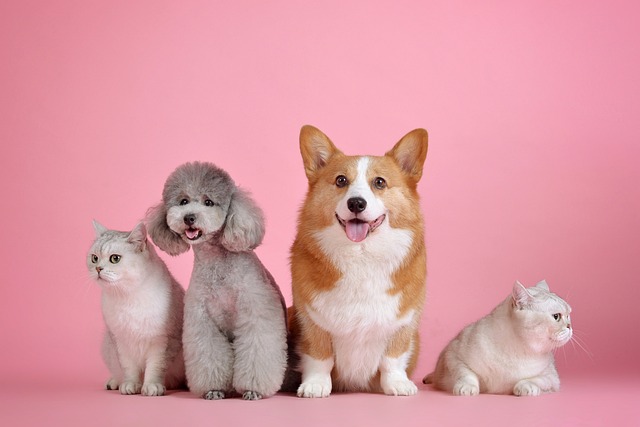
cv2_imshow(img)テスト用の画像をダウンロードします。
- 1行目:犬と猫が写った画像を団運ロードします
- 3行目:画像データを変数に格納
- 5行目:opencvインポート
- 6行目:colab上で画像を表示するライブラリをインポート
- 8行目:opnecvで画像を読み込んで
- 9行目:表示
手持ちデータをテストに使いたいなら
from google.colab import files
uploaded = files.upload()
for filename in uploaded:
content = uploaded[filename]
with open(filename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(content)
if len(uploaded.keys()):
IMAGE_FILE = next(iter(uploaded))
print('Uploaded file:', IMAGE_FILE)
img = cv2.imread(IMAGE_FILE)
cv2_imshow(img) colab上で手持ちデータで試すときは、上のコードを実行してください。ファイル選択というボタンを押してPC上の画像データを選びましょう。
- 1行目:colab上でファイル管理するライブラリをインポート
- 2行目:アップロードするオブジェクト
- 4~11行目:画像をアップロードして、colab上に保存します。ファイル名は一緒です。
- 14行目:保存した画像をopncvで読み込んで
- 15行目:表示します
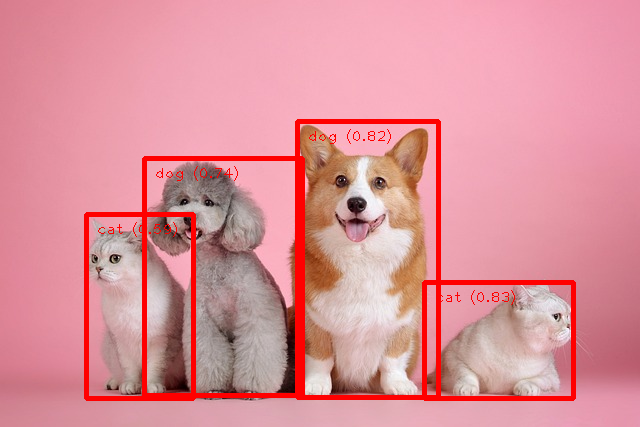
こんな画像です、犬のような猫もいますがどうでしょう

物体検知実行して結果表示
# STEP 1: Import the necessary modules.
import numpy as np
import mediapipe as mp
from mediapipe.tasks import python
from mediapipe.tasks.python import vision
# STEP 2: Create an ObjectDetector object.
base_options = python.BaseOptions(model_asset_path='efficientdet.tflite')
options = vision.ObjectDetectorOptions(base_options=base_options,
score_threshold=0.5)
detector = vision.ObjectDetector.create_from_options(options)
# STEP 3: Load the input image.
image = mp.Image.create_from_file(IMAGE_FILE)
# STEP 4: Detect objects in the input image.
detection_result = detector.detect(image)
# STEP 5: Process the detection result. In this case, visualize it.
image_copy = np.copy(image.numpy_view())
annotated_image = visualize(image_copy, detection_result)
rgb_annotated_image = cv2.cvtColor(annotated_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
cv2_imshow(rgb_annotated_image)本題の物体検知部分です
- 2~5行目:numpyとmediapipeをインポート
- 8~11行目:物体検知のオブジェクト作成(設定)です
- 8行目:モデル指定です。ダウンロードしておいた、Efficient Detのファイルを指定します。
- 9行目:画像物体検知向けの設定です。使用するモデルを指定して、判断するための閾値を0.5に指定します。
- 10行目:物体検知のオブジェクトを作っておきます。
- 14行目:画像データを読み込んで
- 17行目:物体検知実行
- 20行目:元画像をコピーしておいて
- 21行目:結果表示の関数を使って、バウンディングボックスとラベル、スコアを画像に書き込みます
- 22行目:opencv形式のGBRからフツーのRGBに並び替えて。opncvもRGBにならないかな~~~
- 23行目:結果表示
結果はこんな感じです。完璧です。。。横向いている猫は無理かな~と思ったのですが。
まとめ
MediaPipeで学習済みモデルを使って、物体検知を行うサンプルコードを紹介しました。
かなり簡単に物体検知ができますので、皆さんも試してください。
可視化のコードの方が長いくらいですね。


